Asexual Reproduction
It is a kind of reproduction in which new individuals are formed from a single parent. There may or may not be gamete formation but there is no fusion of gametes. It is also known as uniparental mode of reproduction. The young ones formed through this process are exact copies of their parents. So they are also called clones of their parents. The members of the group of clones are called ramets.
Types of asexual reproduction
There are many types of asexual reproduction. These are: fission, sporulation, budding, fragmentation and regeneration.
Fission
It is a type of asexual reproduction in which an individual divides into two or more individuals. It may be binary fission or multiple fission.
Binary Fission :
It is a mode of asexual reproduction in which the parent body divides into two equal halves. It may be simple, longitudinal, transverse or oblique binary fission.
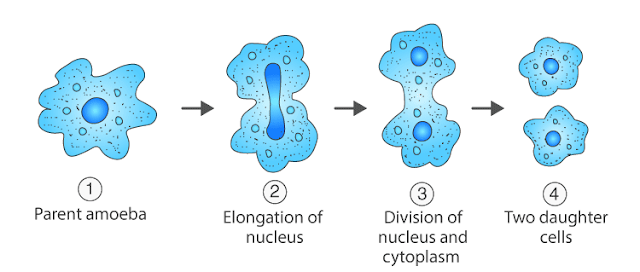
Simple Binary Fission (irregular binary fission) : In this type of binary fission the parent body may divide through any plane. But the division of the cytoplasm is always perpendicular to the division of nucleus. It occurs in amoeba, bacteria etc.
Longitudinal Binary Fission : The parent is divided into two equal halves longitudinally, e.g., Euglena.
Transverse Binary Fission : In this type of binary fission the body of the parent divides transversely into two dissimilar halves, e.g., in Paramecium.
Oblique Binary Fission : In this type the plane of division is oblique as in Ceratium.
Multiple Fission:
In the multiple fission parent cell divides into many nuclei. Each daughter nucleus is then surrounded by a small mass of cytoplasm and the new structure so formed may be a spore, schizont, gamont etc. These structures later on form new organisms when the conditions are favourable. Multiple fission occurs in Amoeba, Plasmodium, Monocystis, etc.
Multiple Fission In Amoeba: In Amoeba multiple fission occurs by sporulation.
Sporulation
It is a kind of multiple fission. Sporulation is the process of formation of minute structures called spores. The process of formation of spores is known as sporulation. It is seen in amoeba.
During unfavorable conditions amoeba withdraws its pseudopodia and secretes a three layered hard covering. It is known as cyst. In encysted condition the amoeba produces a number of minute amoebae called pseudospores.
But sometimes the amoeba does not form a cyst. It produces a number of spores or ensheathed amoebae. This process is called sporulation. The spores on favorable condition form small amoebae.
Budding
A bud is an outgrowth formed from external or internal parts of the body. A bud may be unicellular or multicellular. It is formed by the process of mitosis. The process of formation of buds is called budding. It is a method of asexual reproduction in many lower organisms. The buds on maturity form the separate organisms. The buds are of two types:-
External buds or Exogenous buds
In this type the bud grows externally on the surface of the body. The bud may split away from the parent and lead on independent life as in Hydra. Sometimes the buds remain attached to the parent body and form a colony as in Scypha.
Endogenous or internal buds or gemmules
In this type a bud or an outgrowth is formed within the parent body. The internal buds are called gemmules. A gemmule consists of a mass of undifferentiated cells called archeocytes. These are covered by a protective coat of amphidisc spicules. A micropyle is present on one side of the gemmule. On favourable conditions archeocytes come out of the gemmule through micropyle and form new organisms. These gemmules help in perennation and dispersal. Gemmules are formed in fresh water sponges such as “Spongilla".
Fragmentation
It is a kind of asexual reproduction in which the parent body breaks into two or more parts called fragments. This process is called fragmentation. Each fragment develops into a whole organism. It occurs in flatworms e.g., microstomum, some coelentrates, sponges, star fish etc.
Regeneration
Regeneration is a kind of asexual reproduction in which the complete organism is formed from a body segment. Such a type of regeneration is called morphollaxis. Sometimes only the lost body part is formed by regeneration. Such regeneration is called epimorphosis. Regeneration was first discovered in Hydra by Trembley (1740).









Comments
Post a Comment